De-Ammonification Control with UV Optical Scanning Nitrite/Nitrate Probe
Problem
The Land van Cuijk WWTP installed a struvite reactor followed by a de-ammonification reactor in 2015 to treat their own centrate from the sludge dewatering as well as leachate water from the neighboring landfill. To control the de-ammonification process, the plant needs a full scale, reliable, and accurate online measurement solution.
Solution
Hach® provided a range of online measurements to control the oxygen, ammonium, pH, nitrite, and nitrate concentrations in real time. This gives the customer the confidence to control the de-ammonification process.
Benefits
Thanks to Hach’s online measurement solutions, Land van Cuijk can control the de-ammonification process at the plant, achieving >90% ammonia removal while the UV scanning probe controls unwanted high nitrite and nitrate concentrations.
Background
Water company Aa en Maas operates seven wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in the Netherlands. Land van Cuijk is one of the seven WWTPs with a maximum hydraulic capacity of 8,000 m3/h and a treatment capacity of 175,000 population equivalent. In 2016, the plant finished a project to build and operate a new de-ammonification process. The de-ammonification process treats rejection water from the plant’s sludge dewatering process and leachate from a landfill nearby.
To treat these two streams, the plant utilises a struvite reactor and the DEMON® de-ammonification process. By adding magnesium, the struvite reactor converts phosphate and ammonium into fertiliser. Next, high concentrations of ammonium are removed by the DEMON® reactor.
Land van Cuijk WWTP Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Ammonium in Centrate | ≈ 1500 mg/L |
| Ammonium in Leachate | ≈ 560 mg/L |
| Ammonium out DEMON® reactor | ≈ 90 mg/L |
| Total N-Removal (%) | > 80% |
| Phosphate in Centrate | ≈ 700 mg/L |
| Phosphate out Struvite reactor | ≈ 80 mg/L |
| Total P-Removal in Struvite reactor (%) | > 70%* |
| Struvite Production | ≈ 250 Kg/Day |
The De-Ammonification Process in General
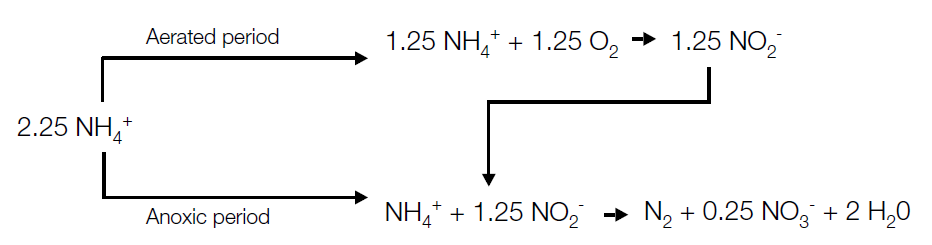
The de-ammonification process is a cost-effective strategy plants can use to replace conventional nitrification/denitrification for the removal of nitrogen compounds from wastewater containing high concentrations of ammonia. The method uses the biological process of nitritation and autotrophic de-ammonification. The process converts approximately 50% of available ammonia to nitrite. De-ammonifying bacteria are used to convert remaining ammonia, together with the produced nitrite, into nitrogen gas.
The benefits of de-ammonification in comparison to nitrification/denitrification are:
- Approximately 60% less energy consumption due to shorter oxidation cycle.
- De-ammonification bacteria consume CO2 as a carbon source. Therefore, no carbon needs to be dosed, making the process less expensive.
- Due to the autotrophic process, the growth rate of the de-ammonification bacteria is very slow and therefore reduces the cost for treating surplus sludge.
Solutions & Improvements
To properly facilitate de-ammonification in the DEMON® reactor, the WWTP installed multiple online measurement points to provide accurate input in real time for oxygen, ammonium cation, pH, nitrite, and nitrate. To accomplish this, the plant installed a Hach solution comprised of:
- NX7500, Scanning Sensor, UV-range
- Amtax sc, Ammonium Analyser
- Phosphax sc, Phosphate analyser
- Nitratax sc, Nitrate Sensor (only in mainstream WWTP)
- Filtrax, Sample Filtration System
- Solitax sc, Suspended Solids sensors (in sludge dewatering process)
- LDO Probes, Dissolved Oxygen
- SC1000 Controller
- DR3900, Laboratory Spectrophotometer
- Bühler Samplers
Critical to the de-ammonification process, the NX7500 Sensor offers optical UV scanning measurements in real time for nitrite and nitrate concentrations. This is without sampling or preparation of test samples, making the measurement process for the DEMON® plant simpler and more accurate. In other WWTP applications, the NX7500 sensor can handle additional parameters in addition to NO3-N and NO2-N, including organics (COD, BOD & TOC) and other parameters.

Conclusion
With online measurements, Land van Cuijk achieved real-time measurement and control. This results in approximately 90% ammonium removal in the DEMON® reactor, helping to keep the entire WWTP plant of Land van Cuijk under its permit limits and its processes under control.
DEMON® is a registered tradename; SWECO the Netherlands has the license for this technology in several countries of Northwestern Europe.
Additional Resources
Pairing Digital Flow Sensors with the Hach AS950 Automatic Sampler
go to HACH.COMIntroduction When the Hach® AS950 Automatic Sampler launched in 2015, we were excited to offer the option to connect digital flow sensors to the controller. Digital flow sensors can be used for collecting flow proportional samples, as well as triggering...

Maximizing Phosphorus Removal
go to HACH.COMPhosphorus removal plays a critical role in protecting waterways, meeting permit requirements, and managing treatment costs. But optimizing phosphorus treatment isn’t always straightforward, especially when processes, influent conditions, and system...

Optimize Total Suspended Solids (TSS) & Turbidity Measurement
go to HACH.COMAccurate measurement of Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and turbidity is vital for effective water quality management across municipal, industrial, and wastewater environments. Real-time insights into solids concentrations empower operators to improve...
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Cookie Settings | Do Not Sell or Share My Data
©Hach All rights reserved.