Liquid-Phase H₂S Sensor Provides New Insights at Treatment Plants
Problem
Despite causing severe odor, corrosion, and worker safety issues, H2S is still a neglected process parameter at wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). This case study examines how two of Veolia’s French subsidiaries, Klearios and Société des Eaux de Marseille (SEM), gained new insights into the H2S challenges at two WWTPs.
Solution
Liquid-phase H2S sensors were installed at the inlet(s) of two WWTPs in France, to permanently monitor dissolved H2S in the raw sewage. This gave operators a real-time overview of their H2S challenge and helped locate the sources thereof.
Benefits
- Full, dynamic overview of H2S concentrations in sewage from the collection system.
- Profile of separate H2S impacts from multiple inlet sources.
- Proactive and data-driven approach to H2S management.
- Improved worker safety.

Background
H2S is a major challenge in wastewater collection systems where it causes odor and corrosion issues. If the H2S challenge isn’t mitigated, all of these problems are transported to the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), where H2S also poses a significant worker-safety concern. Finally, studies have found that H2S inhibits biological wastewater treatment processes. Yet despite the severity of the issues caused by H2S, it is still largely a neglected process parameter. Existing measurement solutions are unable to provide a dynamic overview of the true H2S challenge. This lack of information limits the plant operators’ capabilities to fully optimize the H2S management at the WWTP.
Challenge
Two Veolia subsidiaries in France wanted to achieve a better understanding of their H2S challenges. At Saint-Nazaire in Western France, Klearios wanted a better overview of H2S in the plant’s combined inlet to see how the existing H2S treatment could be optimized using sensor data. And at Cassis in Southern France, SEM wanted to map H2S from two separate inlet sources — a pressurized line and a gravitational line.
Setup
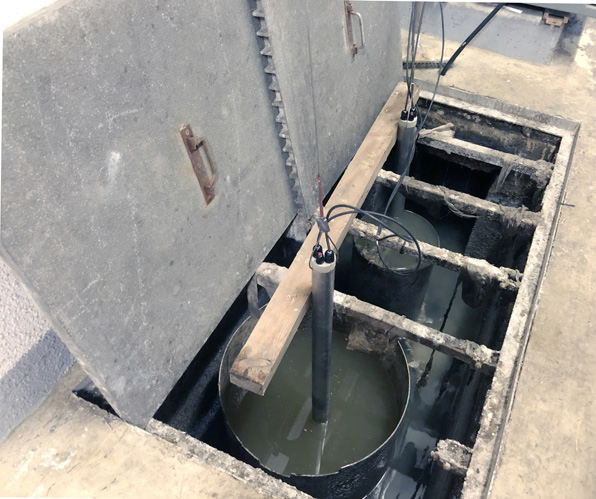
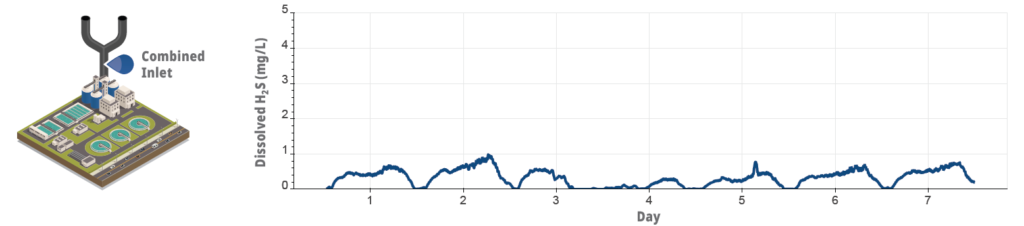
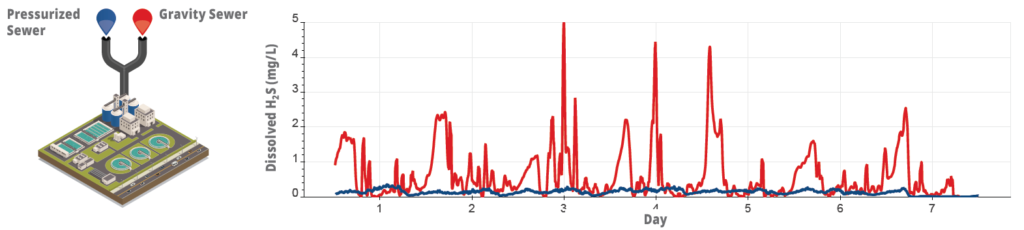
Three Hach® H2S sensors were installed directly in the raw wastewater at the inlets of the two plants in a ‘gatekeeper’-like setup. A single sensor was installed at the combined inlet at the WWTP in Saint-Nazaire, while two sensors were installed at the two influent sources at the WWTP in Cassis.
All sensors were connected to Hach’s cloud-based IoT solution, which provided detailed graphs of the H2S development over time.

Results
In both cases, it was possible to achieve a full, dynamic overview of how H2S impacted the plants. These insights enable future H2S mitigation activities to be started on a fully informed basis. To track the root cause of the issues, the operators could also initiate further measurement campaigns upstream in the collection system.
At the Saint-Nazaire plant, Klearios gained insights into the plant’s combined inlet (blue), which showed regular patterns with varying daily peaks between 0.2 and 1.0 mg/L H2S.
At the Cassis plant, two different H2S profiles were observed from two influent sources. The H2S profile from the pressurized system (blue) followed a predictable pattern with consistently low H2S levels below 0.4 mg/L, while a different profile was observed at the gravitational line (red), where frequent and irregular spikes above 5 mg/L were observed. The flow rate was significantly lower than in the pressurized line, indicating that the effect of the spikes would be less visible on the plant’s combined inlet.
Perspectives
H2S remains a neglected, dangerous, and expensive parameter at the WWTP. Although WWTP operators possess all the tools and techniques needed to mitigate the unwanted gas, readily available data is needed to optimize the effectiveness of the chosen H2S mitigation activities. The Hach H2S sensor delivers this knowledge by providing a true, reliable, and dynamic overview of how H2S impacts the WWTP.
Why is H2S a Problem at Treatment Plants?
- H2S causes rotten-egg odors affecting quality-of-life for nearby residents and staff.
- H2S-induced corrosion significantly reduces the lifespan of valuable plant assets.
- H2S inhibits treatment processes and is a problem in biogas production.
- H2S is a worker safety concern causing several undesirable health effects. The gas is potentially lethal at concentrations above 500 ppm.
Additional Resources
Pairing Digital Flow Sensors with the Hach AS950 Automatic Sampler
go to HACH.COMIntroduction When the Hach® AS950 Automatic Sampler launched in 2015, we were excited to offer the option to connect digital flow sensors to the controller. Digital flow sensors can be used for collecting flow proportional samples, as well as triggering...

Maximizing Phosphorus Removal
go to HACH.COMPhosphorus removal plays a critical role in protecting waterways, meeting permit requirements, and managing treatment costs. But optimizing phosphorus treatment isn’t always straightforward, especially when processes, influent conditions, and system...

Optimize Total Suspended Solids (TSS) & Turbidity Measurement
go to HACH.COMAccurate measurement of Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and turbidity is vital for effective water quality management across municipal, industrial, and wastewater environments. Real-time insights into solids concentrations empower operators to improve...
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Cookie Settings | Do Not Sell or Share My Data
©Hach All rights reserved.