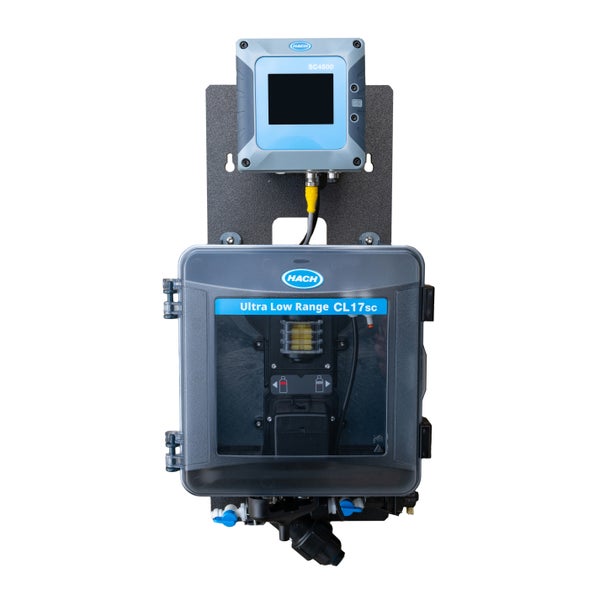
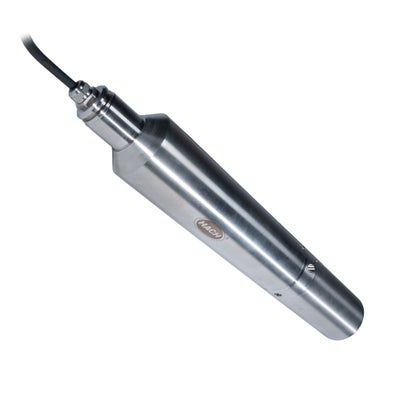
Nitrate Measurement with Hach’s NT3100sc UV Sensor
Background

One of the common goals at a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) is the reduction of nitrogen, as it has negative effects on the water bodies it discharges into such as eutrophication, fish toxicity, and high oxygen consumption. To ensure that the nitrogen concentration in the WWTP discharge meets regulated limits, the nitrification and denitrification processes require optimal control. Therefore, instrumentation needs to be placed in the relevant locations of the plant to measure the different forms of nitrogen to achieve a stable and cost-effective operation. Hach® offers a solution to measure nitrate (NO3) with the NT3100sc UV Nitrate Sensor for process control and monitoring.
Elimination of Nitrogen in Wastewater

Mainly organic nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen are present in the inlet of a WWTP. Through ammonification, organic nitrogen turns into ammonium. This process starts in the sewage system and continues in the treatment plant. When nitrogen arrives at the biological stage, it is largely transformed into ammonium. During nitrification, ammonium is oxidized via nitrite to nitrate, requiring oxygen. In denitrification, nitrate is converted to nitrogen gas that can leave the system, with nitrite as a possible intermediate. Denitrification can be configured as pre-aeration, post-aeration, simultaneous, or intermittent. Success requires sufficient easily biodegradable carbon, optimized internal recirculation, and the absence of dissolved oxygen. Figure 1 illustrates the removal process.
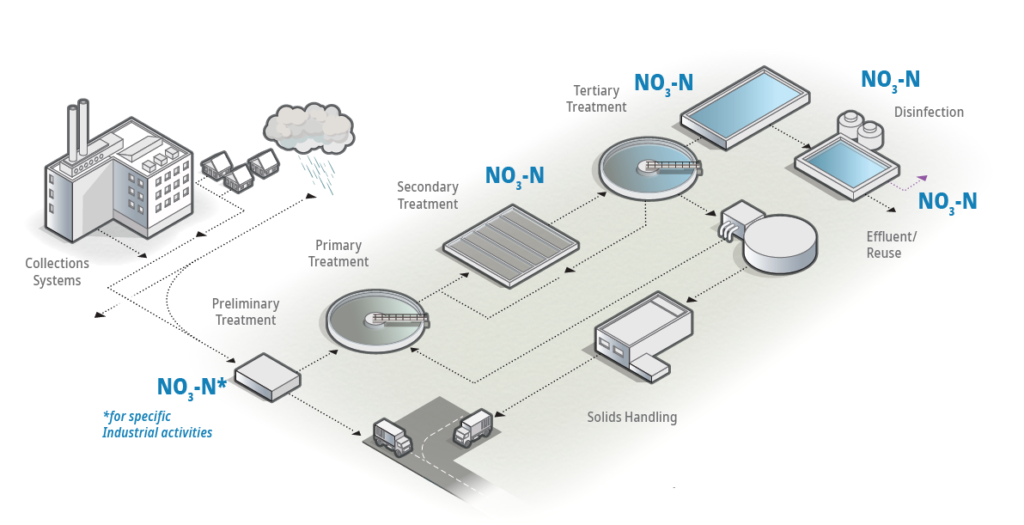
Constant and systematic measurement of individual nitrogen parameters enables long-term stable performance of nitrogen removal and compliance with total nitrogen limits. Measurements can be conducted online and in the laboratory. Figure 2 indicates key measuring points for nitrate in a WWTP.
Online Sensor

The NT3100sc online sensor is based on optical UV measurement to detect nitrate. Path lengths of 1 mm, 2 mm, and 5 mm make it suitable for municipal wastewater, industrial wastewater, drinking water, and reuse processes. An integrated self-cleaning wiper minimizes fouling, while turbidity compensation reduces errors from interference. The sensor is compatible with Hach SC controllers and Claros™, supporting operators with data management and trouble-free operation. Real-time data allows operators to detect process changes early and make adjustments to avoid upsets. With simple handling and easy installation, the sensor is immediately ready for use.
Applications in Municipal Wastewater Treatment
| Treatment Stage | Application | Measuring Point | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | Monitoring inlet | WWTP inlet |
|
| Secondary Treatment | Monitoring denitrification | Denitrification |
|
| Monitoring nitrification | Aeration tank |
|
|
| Monitoring simultaneous nitrification and denitrification | Aeration tank |
|
|
| Monitoring post-denitrification | Denitrification |
|
|
| Monitoring swing zones | Aeration tank |
|
|
| Monitoring deammonification in main stream | Deammonification tank |
|
|
| Effluent | Monitoring of disinfection stage | Disinfection effluent |
|
| Monitoring effluent | WWTP effluent |
|
Key Outcome: The Hach NT3100sc UV Sensor provides reliable, low-maintenance nitrate measurement, supporting stable nitrogen removal, reduced operating costs, and compliance with environmental regulations in wastewater treatment.
Additional Resources
Pairing Digital Flow Sensors with the Hach AS950 Automatic Sampler
go to HACH.COMIntroduction When the Hach® AS950 Automatic Sampler launched in 2015, we were excited to offer the option to connect digital flow sensors to the controller. Digital flow sensors can be used for collecting flow proportional samples, as well as triggering...

Maximizing Phosphorus Removal
go to HACH.COMPhosphorus removal plays a critical role in protecting waterways, meeting permit requirements, and managing treatment costs. But optimizing phosphorus treatment isn’t always straightforward, especially when processes, influent conditions, and system...

Optimize Total Suspended Solids (TSS) & Turbidity Measurement
go to HACH.COMAccurate measurement of Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and turbidity is vital for effective water quality management across municipal, industrial, and wastewater environments. Real-time insights into solids concentrations empower operators to improve...
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Cookie Settings | Do Not Sell or Share My Data
©Hach All rights reserved.




